20 Financial Advantages of Participating in Maritime Industry Alliances

Maritime industry alliances bring together companies to leverage collective resources, share knowledge, and enhance bargaining power. The financial benefits of such collaborations are significant, ranging from reduced operational costs to improved market access. Here, we explore the top advantages of joining maritime industry alliances and how they can contribute to a more profitable and sustainable shipping operation.
* Please send feedback/suggestions to editor @ shipuniverse.com
1. Bulk Purchasing Power
- Description: By joining an alliance, companies can leverage collective purchasing power to negotiate better rates for essential supplies such as fuel, lubricants, spare parts, and equipment.
- Example: An alliance of shipping companies might negotiate a bulk fuel purchase agreement that provides significant discounts compared to individual purchases. This collective bargaining power can lead to substantial savings in operational costs.
- Benefit: Reduced cost of goods and services through economies of scale.
2. Shared Research and Development Costs
- Description: Maritime industry alliances allow member companies to pool their resources for research and development (R&D), spreading the financial burden across multiple entities.
- Example: Several shipping companies within an alliance may jointly invest in developing a new, more fuel-efficient engine technology. The shared cost of R&D makes it more affordable for each company while accelerating technological advancements.
- Benefit: Lower R&D expenses and faster innovation, leading to competitive advantages and long-term cost savings.
3. Improved Operational Efficiency
- Description: Alliances often promote the adoption of standardized procedures and best practices, leading to more efficient operations across the board.
- Example: Members of an alliance might standardize their maintenance schedules and operational protocols, resulting in reduced downtime and increased fleet utilization.
- Benefit: Enhanced operational efficiency reduces waste and lowers overall operating costs, improving profitability.
4. Enhanced Market Access
- Description: Being part of an alliance can provide better access to new and existing markets through shared networks, relationships, and resources.
- Example: An alliance may have established connections in emerging markets, enabling member companies to enter these markets more easily and with less risk. This expanded reach can lead to new business opportunities and revenue streams.
- Benefit: Increased market reach and business growth potential without the need for extensive individual investments in market entry strategies.
5. Risk Sharing
- Description: Alliances enable companies to share financial risks associated with large-scale projects, investments, and ventures.
- Example: If several shipping companies within an alliance decide to invest in a new shipping route or port infrastructure, the financial risk is distributed among all the participants rather than borne by a single entity.
- Benefit: Reduced individual exposure to financial risk, making it easier to undertake large projects that could drive growth and profitability.
6. Better Access to Financing
- Description: Financial institutions may perceive alliances as more stable and creditworthy compared to individual companies, leading to improved access to financing options.
- Example: An alliance of shipowners might secure favorable loan terms or lower interest rates for fleet upgrades or expansion projects because lenders view the collective group as a lower risk.
- Benefit: Enhanced financing options at better terms, reducing the overall cost of capital for members.
7. Enhanced Bargaining Power with Service Providers
- Description: Alliances can negotiate better rates and service agreements with ports, logistics providers, and other service providers due to their collective volume and importance.
- Example: A maritime alliance might negotiate reduced port fees or expedited services for its member ships, resulting in lower operational costs and faster turnaround times.
- Benefit: Cost savings and improved service levels, contributing to overall operational efficiency and competitiveness.
8. Collaborative Training and Development Programs
- Description: Alliances can offer shared training and development programs for crew and staff, spreading the cost across multiple companies and improving workforce skills.
- Example: An alliance might develop a comprehensive training program for ship safety and operations, with costs shared among all members. This ensures a consistently high level of competency across the fleet.
- Benefit: Lower training costs and a more skilled workforce, leading to improved operational performance and reduced incidents or accidents.
9. Joint Marketing and Branding Initiatives
- Description: Alliances can pool resources for joint marketing and branding efforts, increasing visibility and market presence at a lower individual cost.
- Example: An alliance might co-sponsor industry events, produce shared marketing materials, or run joint advertising campaigns, spreading the cost among all members while amplifying their reach.
- Benefit: Enhanced brand recognition and market presence at a fraction of the cost of individual marketing efforts.
10. Streamlined Regulatory Compliance
- Description: Alliances can collaborate to ensure compliance with international regulations, sharing the cost of legal advice, audits, and compliance management.
- Example: Members of a maritime alliance may collectively hire regulatory experts to ensure all ships meet environmental and safety standards, thus reducing the individual burden of compliance.
- Benefit: Reduced costs associated with regulatory compliance and minimized risk of fines or sanctions.
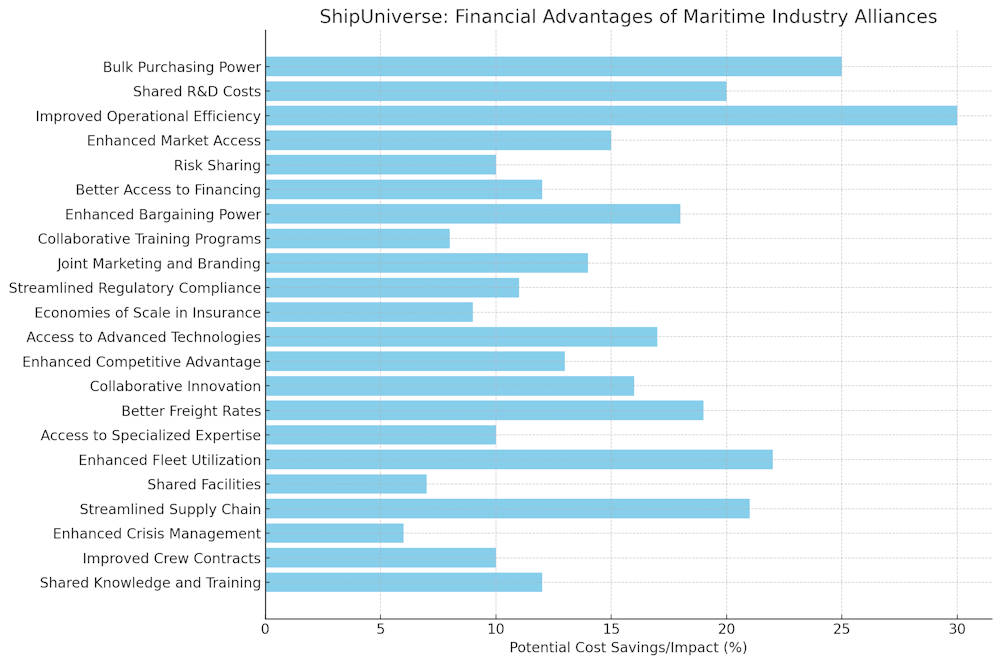
11. Economies of Scale in Insurance
- Description: By grouping together, alliance members can negotiate better insurance terms and rates, benefiting from economies of scale.
- Example: An alliance could secure comprehensive insurance coverage for all member vessels at a lower premium than what individual companies would pay.
- Benefit: Lower insurance costs and enhanced coverage, providing better financial protection at reduced rates.
12. Access to Advanced Technologies
- Description: Alliances can facilitate access to cutting-edge technologies that might be too costly for individual companies to acquire independently.
- Example: An alliance might invest in advanced navigation systems, fuel optimization software, or autonomous shipping technologies, making these innovations accessible to all members.
- Benefit: Access to the latest technologies at a lower cost, enhancing operational efficiency and competitiveness.
13. Enhanced Competitive Advantage
- Description: Alliances can help members stay competitive by sharing market intelligence, industry trends, and best practices.
- Example: Members of an alliance might exchange information on emerging market opportunities or new regulatory changes, enabling them to adapt quickly and maintain a competitive edge.
- Benefit: Improved market responsiveness and strategic positioning, leading to sustained profitability and growth.
14. Collaborative Innovation and Problem Solving
- Description: Alliances foster a collaborative environment where members can jointly address common challenges and innovate together.
- Example: If an alliance faces a common issue such as reducing emissions, members can work together to develop and implement innovative solutions, sharing both the costs and the benefits.
- Benefit: Accelerated innovation and cost-effective problem-solving, leading to improved operational performance.
15. Increased Bargaining Power in Chartering and Freight Rates
- Description: Alliances can leverage their combined capacity to negotiate better chartering terms and freight rates with shippers and charterers.
- Example: An alliance can collectively negotiate higher freight rates or more favorable chartering terms, reducing empty leg costs and increasing overall revenue.
- Benefit: Improved revenue from better-negotiated contracts, leading to higher profitability.
16. Access to Specialized Expertise
- Description: Alliances can provide access to specialized expertise and consulting services that might be too expensive for individual companies to afford.
- Example: An alliance might hire top maritime consultants or legal advisors to assist with complex issues like international trade regulations or environmental compliance, with costs shared among all members.
- Benefit: Reduced consulting and advisory costs while gaining access to high-level expertise, enhancing strategic decision-making.
17. Enhanced Fleet Utilization
- Description: Alliances can optimize fleet utilization by coordinating schedules and routes, reducing idle time and increasing operational efficiency.
- Example: Members of an alliance might share cargo loads or adjust routes to ensure that ships are always carrying optimal cargo loads, thereby maximizing revenue.
- Benefit: Increased fleet utilization and revenue, leading to lower per-unit costs and higher overall profitability.
18. Cost Savings through Shared Facilities
- Description: Alliances can share facilities such as warehouses, maintenance yards, and port terminals, reducing the need for individual investments.
- Example: An alliance might jointly invest in a shared dry dock or maintenance facility, reducing the cost burden for each member and ensuring consistent maintenance standards.
- Benefit: Reduced capital and operational expenditures on facilities, leading to significant cost savings.
19. Streamlined Supply Chain Management
- Description: Alliances can collaborate to create more efficient supply chains, reducing logistics costs and improving delivery times.
- Example: Members might synchronize their supply chain operations to reduce redundancies, lower inventory costs, and improve overall logistics efficiency.
- Benefit: Lower supply chain costs and improved delivery performance, enhancing customer satisfaction and profitability.
20. Enhanced Crisis Management and Resilience
- Description: Alliances can develop joint crisis management strategies, sharing resources and knowledge to better handle emergencies and disruptions.
- Example: In the event of a natural disaster or geopolitical disruption, alliance members can pool resources to ensure continuity of operations, minimizing financial losses.
- Benefit: Improved resilience and reduced financial impact from crises, ensuring more stable and predictable operations.
21. Improved Negotiation Power for Crew Contracts
- Description: Alliances can negotiate better terms and conditions for crew contracts by leveraging their collective bargaining power.
- Example: An alliance might negotiate standardized contracts with labor unions or crew agencies, resulting in more favorable terms and reduced labor costs for all members.
- Benefit: Lower crew costs and improved contract terms, leading to overall cost savings and better workforce management.
22. Shared Knowledge and Training Resources
- Description: Alliances can share knowledge and training resources, reducing the costs associated with individual training programs and ensuring a consistently high level of expertise across member companies.
- Example: An alliance might develop a shared training platform for maritime safety, regulatory compliance, and operational best practices, providing comprehensive training to all member companies at a reduced cost.
- Benefit: Reduced training expenses and a highly skilled workforce, leading to improved operational efficiency and safety.
Participating in maritime industry alliances offers a multitude of financial advantages that can transform the way ship owners manage their fleets. From bulk purchasing power and shared R&D costs to improved operational efficiency and enhanced market access, the benefits are clear and compelling. By collaborating with other industry players, ship owners can not only reduce costs but also drive innovation, improve risk management, and secure better financing options. In an industry where margins can be thin, these alliances provide a strategic pathway to greater profitability and long-term success. Embracing the power of collective effort can ultimately lead to a stronger, more resilient, and more competitive maritime sector.
Maritime Alliances
1. 2M Alliance
The 2M Alliance is a vessel-sharing agreement between Maersk Line and MSC (Mediterranean Shipping Company). This alliance aims to improve service offerings and efficiencies through shared resources and combined networks.
Website: Maersk Line | MSC
2. Ocean Alliance
The Ocean Alliance consists of CMA CGM, COSCO Shipping, Evergreen Line, and OOCL. This alliance focuses on providing comprehensive services across major trade routes, enhancing efficiency and service reliability.
Website: CMA CGM | COSCO Shipping | Evergreen Line | OOCL
3. THE Alliance
THE Alliance includes Hapag-Lloyd, Yang Ming, and Ocean Network Express (ONE). This alliance aims to offer competitive services through a combined fleet, covering major East-West trade routes.
Website: Hapag-Lloyd | Yang Ming | Ocean Network Express
4. Global Shipping Business Network (GSBN)
GSBN is a blockchain consortium that aims to enhance efficiency and transparency in the shipping industry through blockchain technology. Major carriers like COSCO, Hapag-Lloyd, and OOCL are part of this network.
Website: GSBN
5. Digital Container Shipping Association (DCSA)
DCSA is a neutral, non-profit group founded by major ocean carriers to digitize and standardize the container shipping industry. Members include MSC, Maersk, Hapag-Lloyd, and CMA CGM.
Website: DCSA
6. Green Marine
Green Marine is an environmental certification program for the North American marine industry, including shipowners, ports, terminals, and shipyards. The program aims to improve environmental performance through voluntary participation and transparency.
Website: Green Marine
7. Trident Alliance
The Trident Alliance is a coalition of shipping companies and other stakeholders committed to the enforcement of maritime sulfur regulations. This alliance focuses on ensuring a level playing field and promoting environmental sustainability.
Website: Trident Alliance
8. Clean Cargo Working Group (CCWG)
CCWG is a business-to-business leadership initiative involving major brands, cargo carriers, and freight forwarders. The group aims to improve the environmental performance of marine container transport.
Website: CCWG
9. Maritime Anti-Corruption Network (MACN)
MACN is a global business network working to eliminate corruption in the maritime industry. The network includes over 100 companies that collaborate on initiatives to promote transparency and fair practices.
Website: MACN
10. Sea Cargo Charter
The Sea Cargo Charter is a framework for aligning chartering activities with responsible environmental behavior. Signatories include major shipping companies and charterers committed to reducing their environmental impact.
Website: Sea Cargo Charter

Do you have a Maritime Product or Service that may be of interest to Shipowners? Tell us about it here!
Do you have feedback or insights? Please reach out to editor @ shipuniverse.com



