Beating the Heat: Overcoming Summer Challenges in Maritime Operations

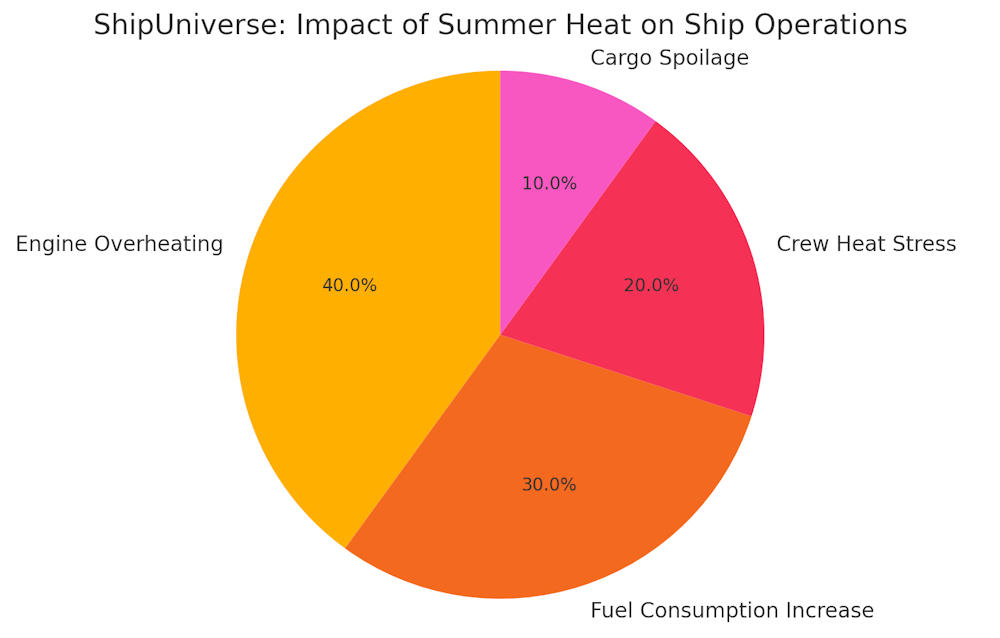
Summer heat can be a real headache for the maritime industry. When temperatures rise, ships and their crews face a host of challenges. High temperatures can make engines overheat, cause fuel consumption to spike, and even put crew members at risk of heat-related illnesses. Plus, perishable cargo like food and plants can spoil quickly in the heat, leading to significant financial losses.
Today we break down the challenges that summer heat brings to ship operations and offer some practical solutions to tackle them. We’ll look at how extreme heat affects ship performance, crew health, and cargo safety. By exploring advanced technologies, maintenance tips, and crew wellbeing practices, we’ll provide actionable advice for the maritime industry. The goal is to help shipping companies navigate the summer heat more effectively and keep operations running smoothly and safely, even when the temperatures soar.
Challenges of Summer Heat on Ship Operations
A. Impact on Ship Performance
1. Engine Overheating
High temperatures pose a significant threat to ship engines, which are designed to operate within specific temperature ranges. When external temperatures soar, it becomes challenging to keep engines cool, leading to a host of problems.
- How High Temperatures Affect Engine Performance:
- Increased Thermal Stress: The metal components of an engine expand more than usual in high heat, causing increased thermal stress. This can lead to warping and reduced efficiency.
- Cooling System Overload: Engines rely on cooling systems to maintain an optimal operating temperature. In extreme heat, these systems can become overwhelmed, failing to dissipate heat effectively.
- Lubricant Degradation: Higher temperatures can cause lubricants to break down faster, reducing their effectiveness and leading to increased friction and wear.
- Consequences of Engine Overheating:
- Potential Failures: Overheating can cause engines to seize, resulting in costly repairs and downtime. In severe cases, it can lead to complete engine failure.
- Reduced Efficiency: Even if the engine doesn’t fail, overheating can reduce its overall efficiency. This means the engine has to work harder, consuming more fuel and producing less power.
- Increased Maintenance Needs: Persistent overheating can accelerate wear and tear, necessitating more frequent maintenance and inspections, adding to operational costs.
2. Increased Fuel Consumption
Hot weather also leads to higher fuel consumption, affecting both the operational costs and environmental impact of maritime operations.
- How Hot Weather Leads to Higher Fuel Consumption:
- Reduced Engine Efficiency: As mentioned, overheating can reduce engine efficiency. An inefficient engine requires more fuel to produce the same amount of power.
- Additional Cooling Demands: To combat high temperatures, ships often need to run additional cooling systems, such as air conditioners and refrigeration units, which consume extra fuel.
- Increased Resistance: Warmer water temperatures can increase the resistance a ship faces while moving, requiring more power—and thus more fuel—to maintain speed.
- Impact on Operational Costs and Environmental Footprint:
- Higher Fuel Costs: Increased fuel consumption directly translates to higher operational costs. Given that fuel is one of the largest expenses for shipping companies, this can significantly impact profitability.
- Environmental Impact: Burning more fuel increases greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to global warming and environmental degradation. Shipping companies face growing pressure to reduce their carbon footprint, making this an important consideration.
- Regulatory Compliance: With stricter regulations on emissions, such as the IMO 2020 sulfur cap, increased fuel consumption can make it harder for ships to comply with environmental standards, potentially leading to fines and other penalties.
Challenges of Summer Heat on Ship Operations
B. Maintenance and Operational Practices
1. Regular Maintenance Schedules
Maintaining a regular maintenance schedule is crucial to ensure that ships operate efficiently and safely, especially during the summer heat.
- Importance of Adhering to Maintenance Schedules:
- Preventative Care: Regular maintenance helps identify potential issues before they become major problems, reducing the risk of engine failures and other heat-related issues.
- Optimal Performance: Ensuring that all systems are functioning correctly keeps the ship running at optimal performance, minimizing the impact of high temperatures.
- Cost Efficiency: Routine maintenance can be more cost-effective in the long run, preventing expensive repairs and downtime.
- Specific Maintenance Tasks to Prevent Heat-Related Issues:
- Cooling System Checks: Regularly inspect and service cooling systems to ensure they are working efficiently. This includes checking coolant levels, cleaning radiators, and inspecting hoses for leaks.
- Lubrication Maintenance: Ensure that all moving parts are adequately lubricated with high-quality lubricants that can withstand high temperatures.
- Engine Inspections: Perform thorough engine inspections to check for signs of overheating, such as warped components or degraded seals.
- Ventilation System Maintenance: Clean and maintain ventilation systems to ensure proper airflow and cooling throughout the ship.
2. Operational Adjustments
Making strategic operational adjustments can help mitigate the effects of summer heat on ship performance.
- Adjusting Sailing Schedules to Avoid Peak Heat Periods:
- Night Sailing: When possible, schedule sailing during cooler night hours to reduce the strain on engines and cooling systems.
- Weather Monitoring: Use advanced weather forecasting tools to plan routes and schedules that avoid extreme heat periods and regions.
- Strategies for Reducing Engine Load During Extreme Heat:
- Speed Reduction: Reduce speed during peak heat to lower engine load and fuel consumption, thus minimizing the risk of overheating.
- Engine Load Distribution: Distribute engine load more evenly across multiple engines, if available, to prevent any single engine from overheating.
- Auxiliary Power Use: Utilize auxiliary power sources, such as battery packs or solar panels, to reduce the load on main engines.
C. Crew Wellbeing Measures
Ensuring the wellbeing of the crew is paramount, particularly during extreme heat conditions.
1. Air Conditioning and Ventilation
Effective air conditioning and ventilation systems are essential to maintain a comfortable and safe environment for the crew.
- Importance of Effective Air Conditioning and Ventilation Systems:
- Comfort and Morale: A well-ventilated and air-conditioned environment helps maintain crew comfort and morale, essential for maintaining productivity.
- Health and Safety: Proper ventilation reduces the risk of heat-related illnesses, such as heat stroke and heat exhaustion.
- Recommendations for Maintaining These Systems:
- Regular Inspections: Conduct regular inspections of air conditioning and ventilation systems to ensure they are operating efficiently.
- Filter Replacements: Replace air filters frequently to maintain good air quality and system efficiency.
- System Upgrades: Consider upgrading to more efficient and modern air conditioning systems that can handle extreme temperatures better.
2. Health and Safety Protocols
Implementing robust health and safety protocols is crucial to protect the crew from the dangers of extreme heat.
- Implementing Health and Safety Protocols to Protect the Crew:
- Hydration: Ensure that crew members have access to plenty of water and encourage regular hydration.
- Rest Breaks: Schedule regular rest breaks, especially during peak heat periods, to prevent exhaustion.
- Cooling Stations: Set up cooling stations with fans, shade, and cold drinks to provide relief from the heat.
- Providing Training on Heat Stress Management and First Aid:
- Heat Stress Training: Educate the crew on recognizing the signs of heat stress and how to prevent it.
- First Aid Training: Provide training on first aid procedures for heat-related illnesses, ensuring that all crew members know how to respond in an emergency.
- Emergency Plans: Develop and practice emergency response plans for heat-related incidents to ensure quick and effective action if needed.
Solutions to Mitigate the Impact of Summer Heat
A. Technological Advancements
1. Advanced Cooling Systems
Implementing advanced cooling systems is essential to combat the effects of extreme summer heat on ships. These systems help maintain optimal operating temperatures for engines and ensure a comfortable environment for the crew.
- Types of Cooling Systems Available for Ships:
- Water Cooling Systems: Utilize seawater to dissipate heat from the engine. This system is efficient but requires regular maintenance to prevent corrosion and blockage.
- Air Cooling Systems: Use air to cool the engine and other components. These systems are less common but can be effective in specific applications.
- Refrigeration-Based Systems: Employ refrigeration cycles to provide cooling. These systems are highly effective and can be used for both engine cooling and crew comfort.
- Hybrid Systems: Combine different cooling methods to optimize performance and efficiency. For example, a hybrid system might use water cooling for the engine and air conditioning for crew areas.
- Benefits of Using Advanced Cooling Technologies:
- Enhanced Efficiency: Advanced cooling systems ensure that engines and other critical components operate within their optimal temperature range, reducing wear and tear and improving overall efficiency.
- Reduced Risk of Overheating: By effectively managing heat, these systems minimize the risk of engine overheating and subsequent failures.
- Improved Crew Comfort: Advanced air conditioning and ventilation systems create a more comfortable living and working environment for the crew, enhancing productivity and morale.
- Energy Savings: Modern cooling technologies are often more energy-efficient, leading to reduced fuel consumption and lower operational costs.
2. Heat-Resistant Materials
Utilizing heat-resistant materials on ships can significantly mitigate the adverse effects of high temperatures. These materials help protect the ship’s structure and components from heat damage.
- Overview of Heat-Resistant Paints and Coatings:
- Ceramic Coatings: These coatings provide excellent thermal insulation and reflectivity, reducing heat absorption on the ship’s surface.
- Intumescent Paints: These paints expand when exposed to high temperatures, creating an insulating barrier that protects the underlying material from heat damage.
- Reflective Paints: Designed to reflect sunlight and reduce heat buildup, these paints help keep the ship’s exterior cooler.
- Advantages of Using These Materials on Ships:
- Protection Against Heat Damage: Heat-resistant coatings and paints shield the ship’s structure from extreme temperatures, preventing warping, cracking, and other heat-related damage.
- Extended Lifespan: By reducing the wear and tear caused by high temperatures, these materials help extend the lifespan of the ship’s components.
- Improved Safety: Heat-resistant materials contribute to overall safety by maintaining the integrity of critical structures and systems, even under extreme heat conditions.
- Energy Efficiency: Reflective and insulating coatings can reduce the need for air conditioning and cooling systems, leading to energy savings and lower operational costs.
Solutions to Mitigate the Impact of Summer Heat
B. Maintenance and Operational Practices
1. Regular Maintenance Schedules
Adhering to regular maintenance schedules is crucial in preventing heat-related issues and ensuring the efficient operation of ships during the summer months.
- Importance of Adhering to Maintenance Schedules:
- Preventative Measures: Regular maintenance helps identify potential problems before they escalate into major issues, reducing the risk of equipment failure.
- Optimal Performance: Routine checks and services keep all systems running efficiently, which is particularly important in extreme heat conditions.
- Cost Savings: Preventative maintenance is generally more cost-effective than emergency repairs and can reduce overall operational costs.
- Specific Maintenance Tasks to Prevent Heat-Related Issues:
- Cooling System Checks: Regularly inspect and maintain cooling systems, including coolant levels, radiators, and hoses, to ensure they function effectively.
- Lubrication Maintenance: Use high-quality lubricants that can withstand high temperatures and ensure all moving parts are adequately lubricated to prevent friction and wear.
- Engine Inspections: Conduct thorough engine inspections to detect any signs of overheating or damage, such as warped components or degraded seals.
- Ventilation System Maintenance: Clean and maintain ventilation systems to ensure proper airflow and cooling throughout the ship, preventing overheating of critical components.
2. Operational Adjustments
Making strategic operational adjustments can help mitigate the effects of extreme summer heat on ship performance and crew comfort.
- Adjusting Sailing Schedules to Avoid Peak Heat Periods:
- Night Sailing: When possible, schedule sailing during cooler night hours to reduce the strain on engines and cooling systems.
- Weather Monitoring: Use advanced weather forecasting tools to plan routes and schedules that avoid extreme heat periods and regions.
- Strategies for Reducing Engine Load During Extreme Heat:
- Speed Reduction: Lower speeds during peak heat can reduce engine load and fuel consumption, minimizing the risk of overheating.
- Engine Load Distribution: Spread the engine load evenly across multiple engines, if available, to prevent any single engine from overheating.
- Auxiliary Power Use: Utilize auxiliary power sources, such as battery packs or solar panels, to reduce the load on main engines, especially during the hottest parts of the day.
C. Crew Wellbeing Measures
Ensuring the wellbeing of the crew is essential, particularly during extreme heat conditions. Implementing effective air conditioning, ventilation systems, and health and safety protocols can make a significant difference.
1. Air Conditioning and Ventilation
Effective air conditioning and ventilation systems are crucial for maintaining a comfortable and safe environment for the crew.
- Importance of Effective Air Conditioning and Ventilation Systems:
- Comfort and Morale: A well-ventilated and air-conditioned environment helps maintain crew comfort and morale, which is essential for productivity.
- Health and Safety: Proper ventilation reduces the risk of heat-related illnesses, such as heat stroke and heat exhaustion, protecting the crew’s health.
- Recommendations for Maintaining These Systems:
- Regular Inspections: Conduct regular inspections of air conditioning and ventilation systems to ensure they are operating efficiently.
- Filter Replacements: Replace air filters frequently to maintain good air quality and system efficiency.
- System Upgrades: Consider upgrading to more efficient and modern air conditioning systems that can handle extreme temperatures better.
2. Health and Safety Protocols
Implementing robust health and safety protocols is crucial to protect the crew from the dangers of extreme heat.
- Implementing Health and Safety Protocols to Protect the Crew:
- Hydration: Ensure that crew members have access to plenty of water and encourage regular hydration.
- Rest Breaks: Schedule regular rest breaks, especially during peak heat periods, to prevent exhaustion.
- Cooling Stations: Set up cooling stations with fans, shade, and cold drinks to provide relief from the heat.
- Providing Training on Heat Stress Management and First Aid:
- Heat Stress Training: Educate the crew on recognizing the signs of heat stress and how to prevent it.
- First Aid Training: Provide training on first aid procedures for heat-related illnesses, ensuring that all crew members know how to respond in an emergency.
- Emergency Plans: Develop and practice emergency response plans for heat-related incidents to ensure quick and effective action if needed.
Summer heat presents a significant set of challenges for the maritime industry, impacting ship performance, crew wellbeing, and cargo safety. However, with proactive measures and advanced solutions, these challenges can be effectively mitigated. By adhering to regular maintenance schedules, making strategic operational adjustments, and prioritizing crew health and safety, shipping companies can ensure smooth and efficient operations even during the hottest months of the year. Embracing technological advancements like advanced cooling systems and heat-resistant materials further enhances the ship’s resilience against extreme temperatures. Ultimately, a comprehensive approach to managing summer heat will not only safeguard the integrity of the vessel and its cargo but also ensure the wellbeing of the crew, leading to more sustainable and successful maritime operations.

Do you have a Maritime Product or Service that may be of interest to Shipowners? Tell us about it here!
Do you have feedback or insights? Please reach out to editor @ shipuniverse.com

